 Suffix Automaton
Suffix Automaton
(string/suffix-automaton.hpp)
- View this file on GitHub
- Last update: 2020-12-11 17:45:42+09:00
- Include:
#include "string/suffix-automaton.hpp"
Suffix Automaton
概要
これはなに?
参考文献:CP-Algorithms uwiさんの記事 迷路さんの記事
図
文字列$S=”\mathrm{nyaan}”$に対応するオートマトンを書いたものが下図
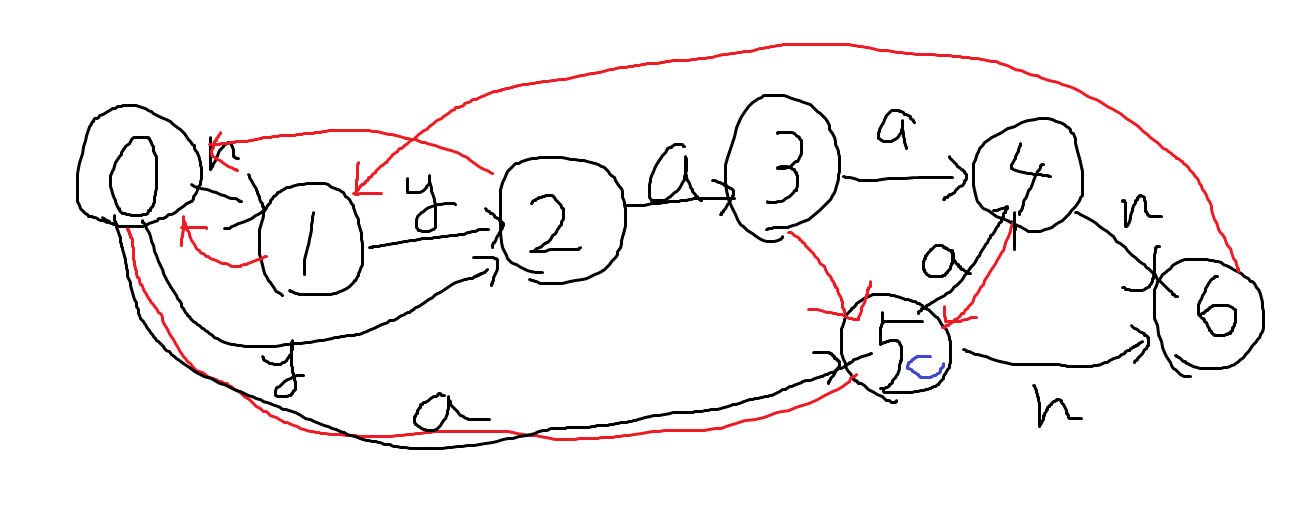
図の説明
- 頂点:部分列と対応した状態
- 図の黒線:次の文字の状態への遷移
- 図の赤線:次の文字の遷移が無かった場合に辿るsuffix link
- 図のc→cloneされたノード
- この説明ではなんのこっちゃという感じなので、$\mathrm{endpos}(T)$を定義して詳しく仕組みを見ていく
$\mathrm{endpos}$
$\mathrm{endpos}$とは?
- 次のように$\mathrm{endpos}$を定義する
- $\mathrm{Suf}(S)$:=文字列$S$のsuffixの集合
- $\mathrm{endpos}(T)$:=$T$が$\mathrm{Suf}(S[0 : i])$に含まれる$i$の集合
- 例:$\mathrm{endpos}(\mathrm{nyaa})=\mathrm{endpos}(\mathrm{aa})=\lbrace 1,3\rbrace$
- $\mathrm{endpos}(T_1)=\mathrm{endpos}(T_2)$であるとき、$T_1$と$T_2$はendpos-equivalentであると呼ぶ
- Suffix Automatonの各ノードは、全てのendpos-equivalentな部分文字列の集合を一つのノードに対応させている
- 言い換えると、Suffix Automatonのノード数は$\mathrm{endpos}(T)$の種類数+初期状態$t_0$の1つである
$\mathrm{endpos}$の性質
- 性質1:部分文字列$u,w(0\lt \mathrm{len}(u) \leq \mathrm{len}(w))$は$u \in \mathrm{Suf}(w)$である場合に限ってendpos-equivalentである。
- 性質2:部分文字列$u,w(0\lt \mathrm{len}(u) \leq \mathrm{len}(w))$は以下の関係が成り立つ。 \(\begin{cases} \mathrm{endpos}(w) \subseteq \mathrm{endpos}(u) & \mathrm{if}\ u\ \in \mathrm{Suf}(w) \\ \mathrm{endpos}(w) \cap \mathrm{endpos}(u) = \phi & \mathrm{otherwise} \end{cases}\)
- 性質3:endpos-equivalentな部分文字列の集合について考える。この集合に含まれる全ての部分文字列をnon-increasingな順番に並び替えると$\mathrm{“nyaan”,”yaan”,”aan”,”an”}$のように長さが1ずつ減少する。
- ここで、Suffix Linkを次のように貼る。
- オートマトンのある状態$v\neq t_0$に含まれる部分文字列のうち最も長いものを$w$とする。この時、$v$に含まれない部分文字列のうち最も長い文字列を$t$とおき、$t$が含まれる状態を$u$として$v$から$u$にSuffix Linkを貼る。
- 頂点に含まれる部分文字列とSuffix Linkのみを図に書いたものが下の図である。
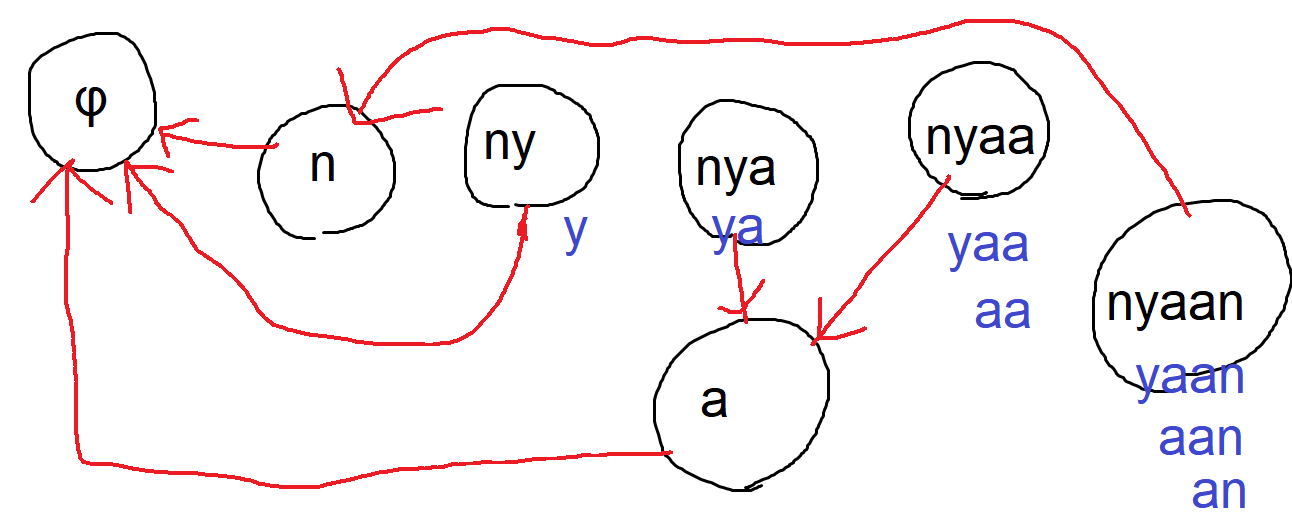
- 性質4:Suffix Linkは$t_0$を根とした木になる。
- 性質5:次のルールのみを用いて木を構築したとき、その構造はSuffix Linkによって作られた木と一致する。
- $\mathrm{endpos}(T_1) \in \mathrm{endpos}(T_2),T_1 \in u,T_2 \in v$であるとき、かつその時に限り$u$は$v$の子孫である。(ただし$\mathrm{endpos}(\phi)=\lbrace{-1,0,\ldots,\mathrm{len}(S)-1\rbrace}$とおく。)
Suffix Automatonの概要
今までのまとめ
-
文字列$S$の部分文字列$T$は$\mathrm{endpos}(T)$の値によっていくつかの集合に分類できる。
-
Suffix Automatonは初期状態$t_0$とendpos-equivalentな集合に一対一対応する状態から構成される。
-
状態$v$に対して一つ以上の部分文字列が対応する。このような部分列のうち一番長いものを$\mathrm{longest}(v)$としてその長さを$\mathrm{len}(v)$とおく。また、一番短い部分文字列の長さを$\mathrm{minlen}(v)$とおく。このとき、状態$v$に対応する全ての文字列は$\mathrm{longest}(v)$のSuffixであり、区間$[\mathrm{minlen}(v), len(v)]$に含まれる全ての長さに対応する全ての部分列のみを含む。
-
状態$v \neq t_0$に対して、長さ$\mathrm{minlen}(v)-1$の$\mathrm{longest}(v)$のSuffixに対応する状態に繋がるリンクをSuffix Linkと定義する。Suffix Linkは$t_0$を根とする木を形成し、同時にこの木は集合$\mathrm{endpos}$の間の包含関係を表している。
-
状態$v \neq t_0$について、$\mathrm{minlen}(v)$はSuffix Linkの接続先$\mathrm{link}(v)$を用いて次のように表される。 \(\mathrm{minlen}(v) = \mathrm{len}(\mathrm{link}(v)) + 1\)
-
任意の状態$v_0$からスタートしてSuffix Linkをたどると$t_0$に到達する。経由した頂点ごとの区間を連結すると連続区間$[0, \mathrm{len}(v_0)]$を得る。
実装
-
TODO:なにも理解していない CP-Algorithmsを読む
-
なんか頂点をcloneするとうまくいくらしい
-
$t_0$から文字列$T$に遷移を辿って状態$v$にたどり着いたとき、$T$は状態$v$に含まれている
性質
-
ノード数/辺数は$\mathrm{O}(\lvert S\lvert)$
-
任意のcloneされたノードnについて、clone元のsuffix link先はnである
#####
Verified with
Code
#pragma once
template <int margin = 'a'>
struct SuffixAutomaton {
struct state {
vector<pair<char, int>> nxt;
uint64_t hit;
int len, link, origin;
char key;
state() : hit(0), len(0), link(-1), origin(-1), key(0) {}
state(int l, char k) : hit(0), len(l), link(-1), origin(-1), key(k) {}
__attribute__((target("popcnt"))) int get_idx(char c) const {
c -= margin;
if (((hit >> c) & 1) == 0) return -1;
if (sorted) {
return _mm_popcnt_u64(hit & ((1ull << c) - 1));
} else {
c += margin;
for (int i = 0; i < (int)nxt.size(); i++) {
if (nxt[i].first == c) return i;
}
}
exit(1);
}
inline int next(char c) const {
int f = get_idx(c);
return ~f ? nxt[f].second : -1;
}
void add(char c, int i) {
c -= margin;
assert(((hit >> c) & 1) == 0);
nxt.emplace_back(c + margin, i);
hit |= 1ull << c;
}
};
inline int next(int i, char c) { return st[i].next(c); }
inline vector<pair<char, int>> &chd(int i) { return st[i].nxt; }
inline int link(int i) { return st[i].link; }
vector<state> st;
static bool sorted;
SuffixAutomaton() : st(1) {}
SuffixAutomaton(const string &S) : st(1) { build(S); }
void build(const string &S) {
int last = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < (int)S.size(); i++) extend(S[i], last);
tsort();
}
int size() const { return st.size(); }
int find(const string &s) const {
int last = 0;
for (auto &c : s)
if ((last = next(last, c)) == -1) return -1;
return last;
}
state &operator[](int i) { return st[i]; }
private:
void extend(char c, int &last) {
int cur = st.size();
st.emplace_back(st[last].len + 1, c);
int p = last;
for (; p != -1 && st[p].get_idx(c) == -1; p = st[p].link) {
st[p].add(c, cur);
}
if (p == -1) {
st[cur].link = 0;
} else {
int q = st[p].next(c);
if (st[p].len + 1 == st[q].len)
st[cur].link = q;
else {
int clone = st.size();
{
state cl = st[q];
cl.len = st[p].len + 1, cl.origin = q;
st.push_back(std::move(cl));
}
for (; p != -1; p = st[p].link) {
int i = st[p].get_idx(c);
if (st[p].nxt[i].second != q) break;
st[p].nxt[i].second = clone;
}
st[q].link = st[cur].link = clone;
}
}
last = cur;
}
void tsort() {
int n = st.size();
vector<int> topo;
{
topo.reserve(n);
vector<vector<int>> base(n + 1);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) base[st[i].len].push_back(i);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
if (!base[i].empty())
copy(begin(base[i]), end(base[i]), back_inserter(topo));
}
{
vector<state> st2;
st2.reserve(n);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) st2.emplace_back(std::move(st[topo[i]]));
st.swap(st2);
}
vector<int> inv(n);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) inv[topo[i]] = i;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
state &s = st[i];
sort(begin(s.nxt), end(s.nxt));
for (auto &[_, y] : s.nxt) y = inv[y];
if (s.link != -1) s.link = inv[s.link];
if (s.origin != -1) s.origin = inv[s.origin];
}
sorted = true;
}
};
template <int margin>
bool SuffixAutomaton<margin>::sorted = false;
/**
* @brief Suffix Automaton
* @docs docs/string/suffix-automaton.md
*/#line 2 "string/suffix-automaton.hpp"
template <int margin = 'a'>
struct SuffixAutomaton {
struct state {
vector<pair<char, int>> nxt;
uint64_t hit;
int len, link, origin;
char key;
state() : hit(0), len(0), link(-1), origin(-1), key(0) {}
state(int l, char k) : hit(0), len(l), link(-1), origin(-1), key(k) {}
__attribute__((target("popcnt"))) int get_idx(char c) const {
c -= margin;
if (((hit >> c) & 1) == 0) return -1;
if (sorted) {
return _mm_popcnt_u64(hit & ((1ull << c) - 1));
} else {
c += margin;
for (int i = 0; i < (int)nxt.size(); i++) {
if (nxt[i].first == c) return i;
}
}
exit(1);
}
inline int next(char c) const {
int f = get_idx(c);
return ~f ? nxt[f].second : -1;
}
void add(char c, int i) {
c -= margin;
assert(((hit >> c) & 1) == 0);
nxt.emplace_back(c + margin, i);
hit |= 1ull << c;
}
};
inline int next(int i, char c) { return st[i].next(c); }
inline vector<pair<char, int>> &chd(int i) { return st[i].nxt; }
inline int link(int i) { return st[i].link; }
vector<state> st;
static bool sorted;
SuffixAutomaton() : st(1) {}
SuffixAutomaton(const string &S) : st(1) { build(S); }
void build(const string &S) {
int last = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < (int)S.size(); i++) extend(S[i], last);
tsort();
}
int size() const { return st.size(); }
int find(const string &s) const {
int last = 0;
for (auto &c : s)
if ((last = next(last, c)) == -1) return -1;
return last;
}
state &operator[](int i) { return st[i]; }
private:
void extend(char c, int &last) {
int cur = st.size();
st.emplace_back(st[last].len + 1, c);
int p = last;
for (; p != -1 && st[p].get_idx(c) == -1; p = st[p].link) {
st[p].add(c, cur);
}
if (p == -1) {
st[cur].link = 0;
} else {
int q = st[p].next(c);
if (st[p].len + 1 == st[q].len)
st[cur].link = q;
else {
int clone = st.size();
{
state cl = st[q];
cl.len = st[p].len + 1, cl.origin = q;
st.push_back(std::move(cl));
}
for (; p != -1; p = st[p].link) {
int i = st[p].get_idx(c);
if (st[p].nxt[i].second != q) break;
st[p].nxt[i].second = clone;
}
st[q].link = st[cur].link = clone;
}
}
last = cur;
}
void tsort() {
int n = st.size();
vector<int> topo;
{
topo.reserve(n);
vector<vector<int>> base(n + 1);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) base[st[i].len].push_back(i);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
if (!base[i].empty())
copy(begin(base[i]), end(base[i]), back_inserter(topo));
}
{
vector<state> st2;
st2.reserve(n);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) st2.emplace_back(std::move(st[topo[i]]));
st.swap(st2);
}
vector<int> inv(n);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) inv[topo[i]] = i;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
state &s = st[i];
sort(begin(s.nxt), end(s.nxt));
for (auto &[_, y] : s.nxt) y = inv[y];
if (s.link != -1) s.link = inv[s.link];
if (s.origin != -1) s.origin = inv[s.origin];
}
sorted = true;
}
};
template <int margin>
bool SuffixAutomaton<margin>::sorted = false;
/**
* @brief Suffix Automaton
* @docs docs/string/suffix-automaton.md
*/